Ear कैसे काम करता है? (How Does the Ear Work?) – Hindi & English
परिचय (Introduction)
.
The ear is one of the most important sensory organs of our body. It helps us hear and maintain balance. It is a complex organ divided into three main parts – outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. Sound waves travel through the air as vibrations, and the ear detects and processes these vibrations.
.
कान (Ear) हमारे शरीर के सबसे महत्वपूर्ण इंद्रियों में से एक है, जो हमें ध्वनि सुनने और संतुलन बनाए रखने में मदद करता है। यह एक जटिल संरचना है, जिसमें बाहरी, मध्य और भीतरी भाग शामिल होते हैं। ध्वनि की तरंगें हवा में कंपन के रूप में आती हैं और कान द्वारा ग्रहण की जाती हैं।
.
.
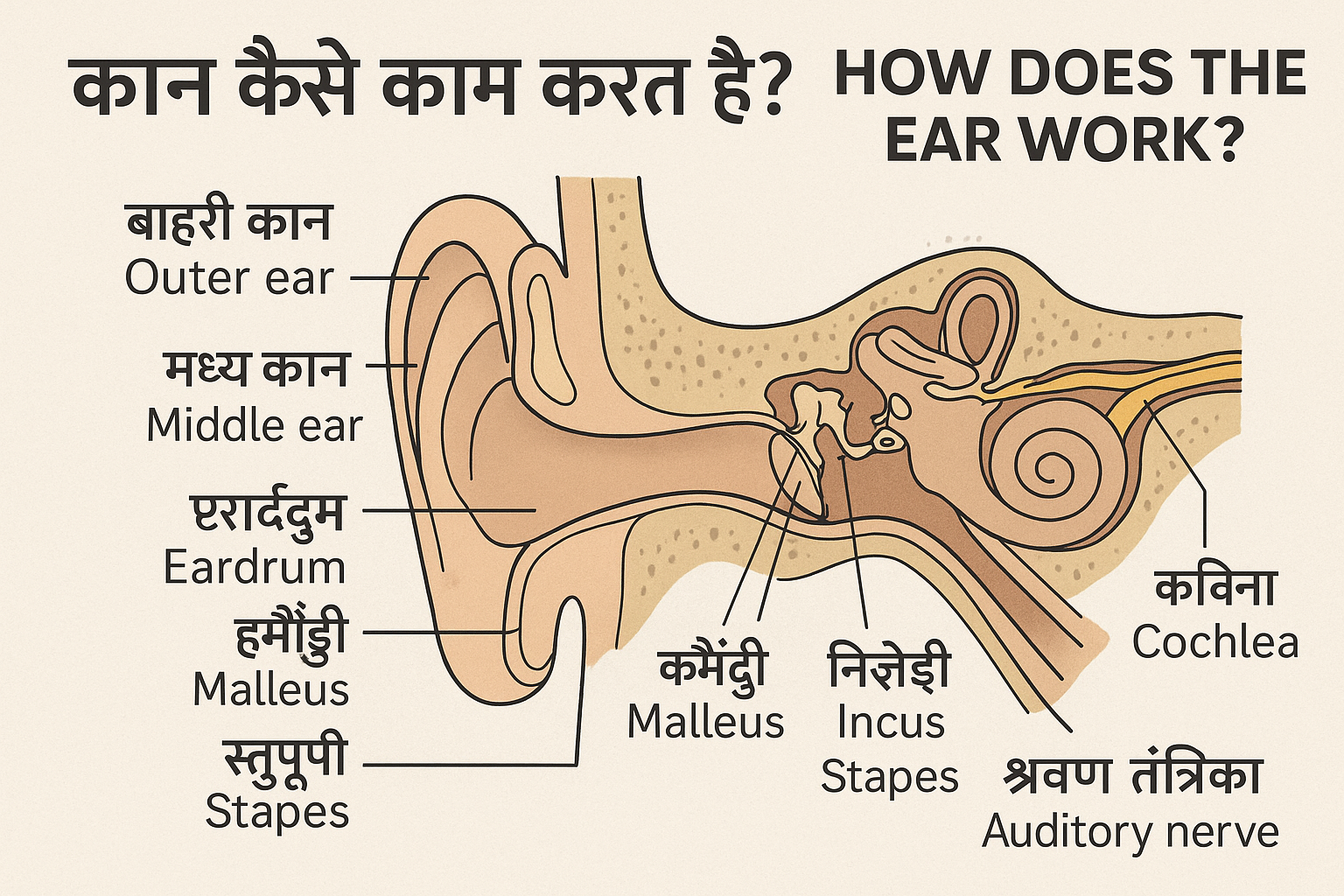
1. कान के भाग (Parts of the Ear)
.
A. बाहरी कान (Outer Ear)
.
It consists of two main parts
.
Pinna: The visible part of the ear that collects sound waves.
.
.Pinna (कर्ण पल्लव): यह कान का दिखाई देने वाला हिस्सा होता है, जो ध्वनि तरंगों को पकड़ता है।
.
External Auditory Canal: A tunnel that carries the sound to the middle ear
.
External Auditory Canal (बाह्य श्रवण नलिका): यह एक सुरंग होती है, जो ध्वनि को मध्य कान तक पहुंचाती है।
.
.
B. मध्य कान (Middle Ear)
.
.The middle ear contains three small bones called ossicles
.
यह भाग तीन छोटी हड्डियों से बना होता है, जिन्हें Ossicles कहा जाता है
.
1. Malleus (हथौड़ी)
.
2. Incus (निहाई)
.
3. Stapes (Stirrup)
.
These bones amplify and transmit sound vibrations to the inner ear. The eardrum vibrates in response to sound waves.
.
ये हड्डियाँ ध्वनि कंपन को अंदर की ओर पहुंचाती हैं। यहाँ एक पतली झिल्ली होती है जिसे Eardrum (कर्णपटह) कहते हैं, जो ध्वनि कंपन से हिलती है।
.
.
C. भीतरी कान (Inner Ear)
.
The inner ear has two major parts
भीतरी कान में दो मुख्य भाग होते हैं
.
1. Cochlea: Converts sound vibrations into electrical signals
1. Cochlea (घोंघा): यह ध्वनि तरंगों को विद्युत संकेतों में बदलता है।
.
2. Vestibular System: Maintains balance and body position.
2. Vestibular System (संतुलन तंत्र): यह शरीर के संतुलन को नियंत्रित करता है।
.
.
2. कान कैसे काम करता है? (How Does the Ear Work?)
.
Step-by-Step Process
.
1. ध्वनि का प्रवेश (Entry of Sound)
.
Sound waves travel through the air and are captured by the pinna. They then move through the auditory canal and strike the eardrum.
.
ध्वनि तरंगें हवा के माध्यम से यात्रा करती हैं और Pinna द्वारा पकड़ी जाती हैं। फिर वे श्रवण नलिका से गुजरकर कर्णपटह से टकराती हैं।
.
2. कंपन और हड्डियों की गतिविधि (Vibration and Bone Movement)
.
The eardrum vibrates, causing the ossicles to move. These bones amplify the sound and transfer it to the inner ear.
कर्णपटह ध्वनि के कारण कंपन करता है, जिससे ossicles हिलने लगते हैं। ये हड्डियाँ ध्वनि को और अधिक बढ़ाकर भीतरी कान तक पहुंचाती हैं।
.
.
3. घोंघे में परिवर्तन (Conversion in Cochlea)
.
The cochlea is filled with fluid and hair cells. These convert vibrations into electrical signals that can be interpreted by the brain.
.
घोंघा एक तरल भरी संरचना है, जो ध्वनि कंपन को विद्युत संकेतों में बदलती है। इसमें छोटे-छोटे बाल (hair cells) होते हैं जो कंपन को पहचानते हैं।
.
.
4. मस्तिष्क तक संकेत (Signals to the Brain)
.
The electrical signals from the cochlea are transmitted to the brain via the auditory nerve, where they are interpreted as sound.
.
घोंघे से उत्पन्न विद्युत संकेत श्रवण तंत्रिका (Auditory Nerve) द्वारा मस्तिष्क को भेजे जाते हैं, जहाँ उनका विश्लेषण होता है और हमें ध्वनि सुनाई देती है।
.
3. संतुलन में कान की भूमिका (Role in Balance)
.
The semicircular canals in the inner ear send information about head motion and body position to the brain. When you move your head, fluid in these canals shifts, helping maintain balance.
.
भीतरी कान में स्थित सेमिकर्कुलर कैनाल्स (Semicircular Canals) शरीर के गति और स्थिति की जानकारी मस्तिष्क तक भेजते हैं। जब सिर हिलता है, तो इन कैनाल्स में तरल भी हिलता है, जिससे संतुलन बना रहता है।
.
4. सुनने में समस्या के कारण (Causes of Hearing Problems)
.
1. Excessive noise
1. अत्यधिक शोर
.
2. Ear infections
2. कान में संक्रमण
.
3. Aging
3. उम्र बढ़ना
.
4. Injury
4. चोट लगना
.
5. Genetic factors
5. अनुवांशिक कारण
.
.
5. कान की देखभाल कैसे करें (How to Take Care of Your Ears)
.
Avoid loud noises
तेज आवाज से बचें
.
Clean ears gently
कानों की सफाई सावधानी से करें
.
Limit use of earphones
ईयरफोन का सीमित प्रयोग करें
.
Get regular ear check-ups
समय-समय पर कान की जांच कराएं
.
.
The ear is not only responsible for hearing but also for maintaining balance. Proper ear care is essential because once hearing is lost, it is often difficult to restore.
.
कान केवल सुनने का माध्यम नहीं है, बल्कि यह हमारे संतुलन का भी केंद्र है। इसकी देखभाल करना बहुत जरूरी है, क्योंकि एक बार सुनने की शक्ति कम हो जाए तो उसे वापस लाना मुश्किल होता है।
.




















